Glenn Mantel of Inergi Agroscience describes an agrochemical solution that may improve the yield, quality, and natural defense system of crops, along with reduced grow cycle length, and need for additional agrochemicals. Read for more details!

The following is an article produced by a contributing author. Growers Network does not endorse nor evaluate the claims of our contributors, nor do they influence our editorial process. We thank our contributors for their time and effort so we can continue our exclusive Growers Spotlight service.
In simplest terms, a colloid is defined as a solution containing nano-sized particles that remain evenly distributed throughout the solution, and do not settle to the bottom or dissolve. (A “nanometer” is a billionth of a meter.) Examples of naturally-occurring colloids are milk, blood, and even dust in the air.
Colloids, when added to agrochemical solutions (such as water-based fertilizers, herbicides, insecticides, and pesticides), will surround and break up the compounds to form Micelles, whose extremely small size and very high surface-area-to-volume ratio, enable them to easily penetrate and deliver these agrochemicals much more efficiently to the plant’s cells.
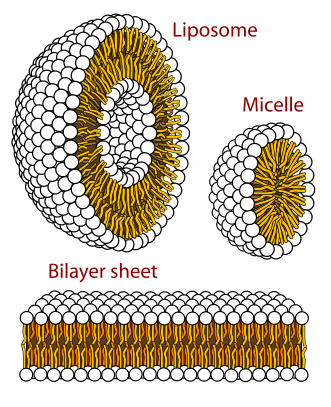
Micelles are formed due to the presence of lipids (fats) in the solution, and due to a unique dual-electrical charge, micelles can be soluble in water. Think of the micelle as a tennis ball, with the agrochemicals held in place on the inside. Micelles are unique in that they have both negatively and positively charged ends. The negative end (which is hydrophilic, or attracted to the water) faces outwards, towards the water solution and the positive end (which is hydrophobic, or repelled by water) faces inwards, thereby suspending the agrochemicals inside.2, 3
Because the outside of the Micelle is attracted to water and repelled by other Micelles, the Micelle actively seeks out water molecules and becomes “hyper-mobile”, enabling the agrochemical molecules on the inside, which normally don’t like water, to be dissolved in water.
If you think about your standard agrochemicals, they often contain surfactants. A surfactant4 is a “surface acting agent,” which reduces the surface tension of water, and is a type of adjuvant5 that helps to disperse the agrochemicals. Surfactants are used in a variety of applications and assist with: cleaning, wetting, dispersing, emulsifying, foaming and anti-foaming.
When highly diluted with water, colloids can significantly reduce surface tension and work as a dispersing agent that carries the micelle’s active ingredients more effectively than common surfactants.
Most commercial adjuvants must be able to penetrate beyond the waxy cuticle surface of leaves in order to be effective. The challenge for most agroscience companies has been getting their adjuvants to penetrate immediately and directly to the xylem and phloem, which are the “veins and arteries” of a plant. By reaching the plant’s xylem and phloem, chemicals can be distributed throughout the plant more effectively and evenly, which experts agree is the optimum delivery method.
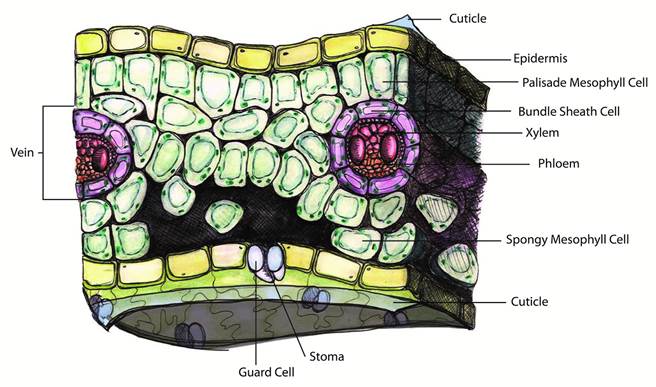
Because micelles are only nanometers in size, they can take agrochemicals that would rarely reach the plant’s vascular system by themselves and directly transport them to the xylem and phloem Therefore, there are some serious benefits for cannabis growers in using a colloidal-based crop enhancement solution:
- Better nutrient and chemical transport and delivery for healthier, hardier plants
- Reduces the total amount of necessary chemical inputs
- Provides crop protection management to optimize plant growth, regardless of biotic or abiotic stress
- Raises Brix (sugar content) levels, resulting in bigger buds with more resin
- Induces rooting and foliage, resulting in earlier harvest and longer grow cycles
References
- Colloids - Physical and Theoretical Chemistry Textbook: https://tinyurl.com/y7s8qwsz
- Micelles - Encyclopaedia Brittanica: https://www.britannica.com/science/micelle
- Micelles - Wikibooks: https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Structural_Biochemistry/Lipids/Micelles
- Surfactants – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Surfactant
- Adjuvants - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Agricultural_spray_adjuvant
10 Best Gift Ideas for Cannabis Connoisseurs and Growing Aficionados (2022)
December 7, 2022Developing and Optimizing a Cannabis Cultivation System
December 14, 2021Dealing with Insomnia: How Can CBD Help?
December 10, 2020Your Guide to Sleep and CBD
December 7, 2020
Do you want to receive the next Grower's Spotlight as soon as it's available? Sign up below!
Resources:
Want to get in touch with Inergi Agrosciences? They can be reached via the following methods:
- Website: http://www.inergigroup.com/
- Email: info@inergicorp.com

Do you have any questions or comments?

About the Author
Glenn Mantel is the Director, Americas for Inergi AgroScience, the leading global manufacturer of organic colloidal concentrate formulations. He is a certified sustainable organic farmer who owned and operated a tropical hardwoods business based in Costa Rica, with clients around the world. He is now focusing his knowledge and experience in the cannabis and produce sectors.